Impact of the implementation of visualization technologies on the real online sales process of a luxury accessory production.
By Aleksei Shestakov, Chairman of the Board & CMO, Digital Tails Group, IEEE Member.
The introduction of visualization technologies, such as 3D configurators, has been widely recognized as having a measurable impact on the efficiency of online sales and overall business performance. Numerous reports from manufacturers and technology providers highlight these effects. What distinguishes the present study is that it constitutes a practical, data-driven investigation of an actual implementation of visualization technology within the operations of a luxury accessory manufacturer. The analysis addresses not only the direct influence on sales performance but also the indirect effects on customer behavior and operational efficiency. This article presents the applied research methods and the corresponding results.
The production of luxury accessories can be conceptualized as the transformation of raw materials into wearable artifacts of personal identity. Within the client’s workshop, each item undergoes individualized processes of cutting, stitching, and finishing, resulting in objects designed for consumers who attribute equal value to both the material qualities of the product and the craftsmanship embedded in its production. The business model has historically expanded not through economies of scale but rather through the delivery of highly personalized outputs. This approach, while central to brand differentiation, introduces significant operational complexity.
Conventional e-commerce platforms are not optimized for this degree of product individualization. Consumers increasingly require the ability to preview outcomes prior to purchase, to conduct comparative evaluations of design alternatives, and to adjust parameters iteratively. The absence of such capabilities imposes friction on both the consumer and the producer, diminishing perceived service quality and increasing transaction costs.
Each order typically incorporates a set of unique variables, such as specific leather types, thread colors, or ornamental details observed through social media. While these variables represent the core of the bespoke value proposition, they simultaneously generate high informational demand. On average, the client’s operations were subject to approximately 300 email interactions per day, each necessitating individualized clarification and verification. This communication overhead resulted in significant processing costs and constrained scalability.
The central challenge thus lay in reconciling personalization with operational efficiency: sustaining the perception of individualized service while enabling customers to autonomously navigate the design space. The solution was the implementation of a three-dimensional (3D) configuration system, designed to replicate material properties, production constraints, and aesthetic options within a digital interface. This approach provides an effective balance between customer agency and production efficiency, establishing a model for digitally mediated mass customization in the luxury accessory sector.
In collaboration with Digital Tails Group, the client transitioned from a reliance on email-based order clarification to a unified digital platform integrated directly into their Shopify storefront. The central component of this transformation was the development of a bespoke three-dimensional (3D) product configurator. This system operates simultaneously as a consumer-facing interface and as an internal production tool, aligning front-end customization with back-end operational requirements.
From the consumer perspective, the configurator replicates the workshop process through an interactive interface that enables the selection of key design parameters:
The system was intentionally designed to reproduce the qualities of a bespoke process while enabling scalability. Three primary design principles underpinned development:
A robust data architecture connects product logic, visual representation, and e-commerce infrastructure in real time. This integration establishes a closed-loop system that simultaneously enhances consumer experience, reduces operational overhead, and ensures consistency between digital design and physical production.
The configurator is implemented on a custom WebGL-based rendering layer, optimized to balance computational efficiency with visual fidelity. The rendering pipeline supports photorealistic representation of materials while maintaining responsiveness for end users. Each configurable parameter is governed by an integrated logic engine that enforces production constraints; incompatible combinations (e.g., non-matching materials and stitching types) are automatically invalidated at the point of selection.
On the e-commerce side, the configurator is natively embedded within the Shopify ecosystem without reliance on third-party plug-ins. Real-time synchronization supports dynamic pricing, variant mapping, cart integration, and seamless checkout processes. This direct integration ensures transactional continuity and minimizes friction in the customer journey.
To maintain operational autonomy, the system incorporates a modular administrative interface designed for non-technical personnel. This panel allows rapid introduction of new product categories, color variations, pricing structures, or stitching patterns. Visual and material assets can be updated, reordered, or archived without developer intervention. The use of dynamic templates further reduces redundancy, enabling replication of logic rules and visual components across product lines. A preview environment allows staff to validate configurations prior to deployment, functioning as a quality assurance mechanism.
The transition from unstructured email communication to structured digital input represents a significant process innovation. Instead of processing vague descriptors (e.g., “brown leather with cream stitching”), the workshop now receives validated, machine-readable specifications that are directly mapped to material identifiers, stock keeping units (SKUs), and internal production codes. This not only accelerates order throughput but also mitigates the risk of rework, delivery delays, and communication overhead. The resulting workflow achieves higher accuracy, reduced error frequency, and greater scalability while preserving the bespoke character of production.
As with most bespoke technology deployments, the implementation extended beyond coding. Effective customization required a comprehensive understanding of the client’s artisanal workflow, encompassing order management, material selection, and the decision-making processes of end customers. This ethnographic and process-oriented knowledge informed the initial system concept and shaped subsequent design choices. Project execution was guided by principles of transparent communication, precise scope definition, and a full-service delivery model. These practices minimized misalignment, reduced the likelihood of scope deviation, and enabled a cooperative development process.
The resulting 3D configurator is now positioned as the central component of the client’s made-to-order value chain. Functioning as a digital extension of the brand’s philosophy, it facilitates customer co-creation while preserving the emphasis on quality craftsmanship. Furthermore, the system architecture was designed for scalability, ensuring adaptability to future expansions in product range and market reach.
The subsequent section examines the measurable impact of this solution on customer behavior and business performance, highlighting both experiential and operational outcomes.
The client’s website features an extensive catalog of ready-made products spanning various price segments. In addition to these products, the manufacturer has launched a line of customizable products, allowing users to select parameters and create unique designs. Instead of classic catalog navigation, the implemented 3D configurator offers product parameter customization without the need to go to other pages. It also visualizes the customization result in an interactive 3D online presentation. Thus, users can immediately see the final result and place an order, while manufacturers immediately receive accurate, documented specifications for each order.
Table 1 shows the results obtained during the first month of the new system’s operation. Let’s analyze and compare these results. First, after launching the 3D configurator for one of our custom products, we observed a significant increase in online sales conversion, rising from 0.77% to 2.05%. This indicates a 2.66-fold increase in online sales, or a 166% growth. At the same time, the average cost to attract a buyer decreased by 62.34%, from £97 to £36.53. Additionally, the average order value increased by 3.33%. Furthermore, all orders now come in online without direct customer support involvement, significantly reducing the manufacturer’s operating costs.
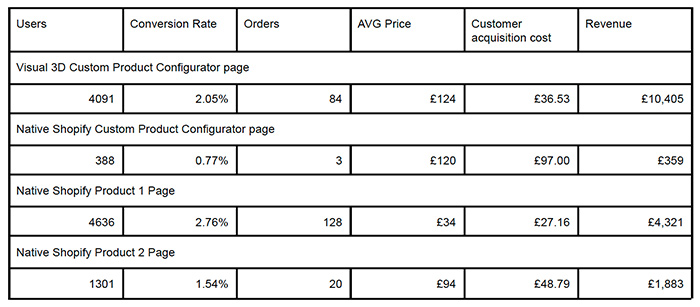
We can also compare our conversion rates with the rates for finished products in the manufacturer’s catalog. For a finished product in the low-cost segment, the conversion rate is 2.76%. This is 34% higher than the conversion rates for custom products using a 3D configurator. The cost of attracting a buyer is £27. However, the cost of the finished product purchased in this case is 72.58% lower.
Conversion rates for high-end finished products vary greatly. At 1.54%, they are 44.02% lower than the conversion rate for low-end products and 24.88% lower than the rate for custom products with a 3D configurator. Meanwhile, the cost of the finished product is 24.19% lower than that of the custom product, while the average cost of attracting a buyer is 33.56% higher. Thus, we can see that the introduction of the 3D configurator significantly improved the online sales of custom products. It also performed well in relation to finished products, ultimately yielding the best financial results in the manufacturer’s online sales structure.
However, while studying the impact of introducing a 3D configurator on online sales indicators, we discovered another factor influencing the manufacturer’s overall online sales: a significant increase in customer engagement, which significantly increases subsequent purchases. Table 2 shows the impact of user visits to specific pages on conversion.
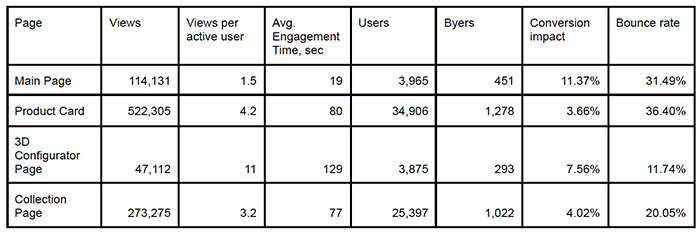
As shown in the table, the home page of the website has the greatest influence on subsequent purchases. Of the users who visited the home page, 11.37% ultimately placed an order. In contrast, users who visited a specific product page only made a purchase 3.66% of the time (not necessarily for that specific product, but for any product in the catalog). Users who visited the 3D configurator page had a 7.56% probability of making a purchase. While this is lower than the home page’s impact, it is significantly higher than the product page’s impact. Thus, implementing the 3D configurator impacts purchases of products from the catalog. Of all visitors to the 3D configurator page, 2.05% purchased a custom product, and 5.51% went to the catalog and purchased other products. When compared with the impact of the product page, these figures show that introducing the 3D configurator increased the overall conversion rate for all of the manufacturer’s products by 3.9%.
In this study, we examined the impact of implementing 3D visualization technology on online sales metrics. We used the real-world implementation of this solution in luxury accessory sales as an example. Our findings revealed that user conversion rates, average order value, and customer acquisition cost collectively yield excellent financial results for the manufacturer. Additionally, we noted two important aspects beyond the direct financial result: a significant reduction in order processing costs for customer support staff and the impact on subsequent purchases by users who decide to buy a ready-made product rather than a custom one. Thus, we conclude that introducing 3D visualization technology and a custom product configurator and integrating them with internal systems, such as an e-commerce platform and CRM system, significantly improves the manufacturer’s business processes and has a substantial economic effect.
REFERRALS
1. Pine, B. J., & Gilmore, J. H. (1999). The Experience Economy: Work is Theatre & Every Business a Stage. Harvard Business School Press.
2. Fogarty, S., & Grewal, D. (2019). 3D Visualization and Product Customization in Online Retailing. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 51, 110–118.
3. Piller, F. T., & Tseng, M. (2017). Mass Customization: A Strategy for Customer Co-Creation and Value Creation. Springer.
4. Bakker, C., & Wang, Z. (2021). The Role of Interactive Product Configurators in Digital Commerce. International Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 21(3), 45–62.
5. Becattini, N., Borgianni, Y., Cascini, G., & Rotini, F. (2020). Value of Virtual Prototypes in Customer Decision-Making: Evidence from Furniture and Fashion Industries. Design Studies, 67, 1–21.
6. Hildebrand, C., Häubl, G., Herrmann, A., & Landwehr, J. R. (2013). When Social Media Can Be Bad for You: Enabling and Preventing Misguided Product Customization. Journal of Marketing Research, 50(3), 339–356.
7. Forbes Insights (2020). The ROI of 3D Visualization in E-commerce. Forbes Research Report.
8. ClickPost (2023). E-commerce Returns Benchmark Report.
9. Threekit Whitepaper (2022). 3D and AR Product Configurators: Driving Engagement and Conversions in Luxury Goods.
About the Author: Aleksei Shestakov – Chairman of the Board & Chief Marketing Officer, Digital Tails Group.
Aleksei Shestakov is an accomplished executive with more than 15 years of experience in marketing, technology, and business strategy. As Chairman of the Board and Chief Marketing Officer of Digital Tails Group, Mr. Shestakov is responsible for guiding the company’s strategic direction, overseeing global marketing initiatives, and driving the development of digital solutions that enable organizations to scale and compete in rapidly evolving markets.
Mr. Shestakov’s professional background spans leadership roles in large-scale media and digital enterprises. He previously served as Marketing Director at Sportbox, one of the largest sports media platforms in Eastern Europe, where he oversaw brand growth and audience expansion. He also directed digital marketing efforts for the Sochi 2014 Olympic Games, one of the most complex and high-profile digital campaigns in international sports.
Since 2015, Mr. Shestakov has concentrated on digital entrepreneurship, founding and advising ventures that apply emerging technologies to transform global industries. He is a member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and an active contributor to discourse on digital transformation, innovation, and business growth.
Scott Ellyson, CEO of East West Manufacturing, brings decades of global manufacturing and supply chain leadership to the conversation. In this episode, he shares practical insights on scaling operations, navigating complexity, and building resilient manufacturing networks in an increasingly connected world.