Dissolved air flotation systems are a spectacular way to treat industrial wastewater with light particles.
By Hydromo- India’s Bespoke Wastewater Treatment Experts
Dissolved Air Flotation system is an advanced wastewater treatment used mostly in the industrial sector in the country to treat wastewater algae, organics, oil and grease. It is very efficient for the reduction of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) present in fat, grease, oil, biological sludge, coloured organic matter, and colloidal material.
It is also excellent for removing oil and grease from industrial wastewater, as mentioned.
DAF has been used for treating drinking water clarification and treatment in several countries like the UK in Europe since the late 1960s and is a common method of choice in drinking water treatment systems in the US too since the 1980s.
In India, though, it is typically used in a wide range of industrial applications to comply and maintain environmental compliance.
What the DAF process does is to separate suspended contaminant particles from liquids, like oil and grease, by bringing them to the surface of the liquid. These light particles are thus easily removed using physical methods.
DAF also facilitates efficient wastewater and process water treatment through flotation with microbubbles.
The incoming wastewater into a DAF system usually requires pre-treatment. Chemical coagulant(s) and/or flocculant(s) are usually added and the adjustment of pH may may also be necessary to ensure optimum operating conditions for DAF.
There are three types of DAF.
These are vacuum flotation, microflotation, and pressure flotation.
All work on a similar system, with minor variations.
Of these pressure flotation is the most important and widely used in water and wastewater treatments today.
Pressure Flotation
Flotation is an extremely critical part of wastewater treatment.
In pressure flotation what happens is that air is dissolved in water under high pressure and released at atmospheric pressure through a nozzle or needle valve to produce small air bubbles.
These air bubbles then make the lighter contaminants and suspended matter in the wastewater float on to the surface of the water in the flotation tank, and these can easily be removed by a skimming device.
This is the reason, Dissolved air flotation is widely used in treating the industrial wastewater effluents from pterochemicals, oil refineries, and chemical plants where the effluent is made of lighter solids.
General water treatments also use DAF for removing colour and organic particles like algae.
Induced gas flotation, a process similar to pressure flotation, is also used for wastewater treatment fairly widely.Froth flotation is also commonly used in the processing of mineral ores.
Flotation Tank- For introducing Bubbles

The flotation tank is divided into two zones: the front zone, where the contact of the dissolved contaminants happen with the flocculants that are introduced to trap them. It is also called the reaction zone.
The other zone is the separation zone. A ‘baffle’ is fixed between the two to control flow.
Small air bubbles are introduced into the contactor reaction zone. This part of the flotation tank is actually designed to form bubble–floc agglomerates.
The bubble size is absolutely critical to form agglomerates.
In DAF, small bubbles are required to achieve an actionable solid–liquid separation. Infact, a bubble size in the range of 50–100 μm is the most suitable for the DAF process.
If the bubbles are larger, they may create turbulence in the flotation tank and, simultaneously, decrease the surface area of the particle-bubble attachment.
To obtain the preferred bubble size, air is dissolved in a saturator under pressure delicately.
The pressure controls the total amount of air introduced into the contact zone at any given time.
Once the bubbles and contaminant particles come into contact through trapping, adhesion, or absorption process in the contact zone, the bubble–floc aggregates move on to the separation zone so that the process water can be clarified.
Separation Zone

This zone is designed to facilitate the rising of the bubble–floc aggregates to the surface of the flotation tank and float as a thick layer of sludge so it can be withdrawn.
The clarified and treated water/wastewater is withdrawn from the bottom of the separation tank.
This process makes the bubble-floc aggregates that do not reach the surface are swept out with the clarified water and these are then re-directed to another flotation tank for separation.
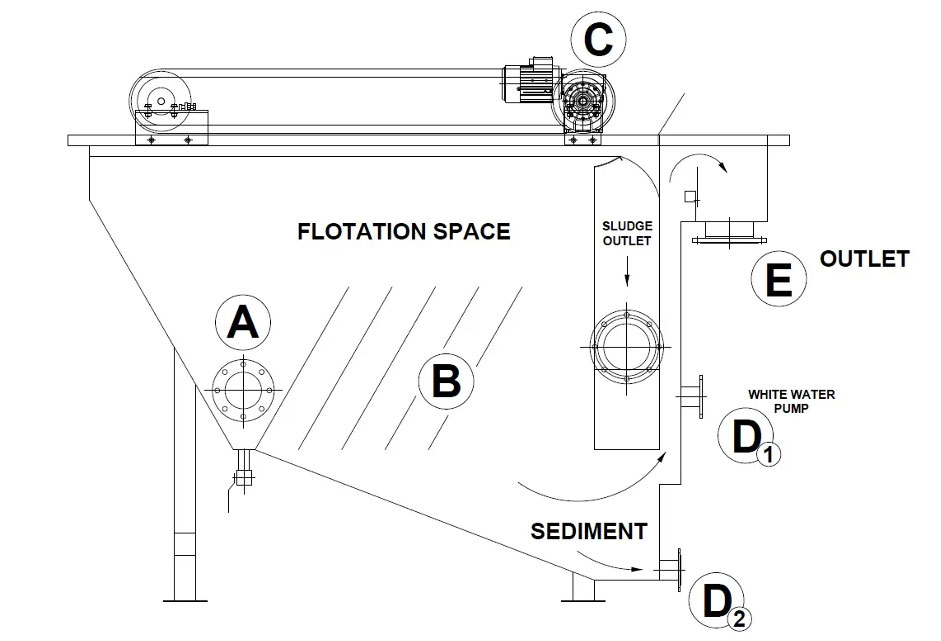
(A) The effluent enters the flotation tank clarification chamber
(B) Tiny air bubbles are released from diffuser nozzles into this chamber pre effluent entry
(C) These micro-bubbles attach to the solid contaminants or chemical flocculants. This causes the impurities like oil and grease to float to the surface and these are then trapped and removed using a mechanical skimmer
(D1) The skimmer consists of a series of paddles or flights in the flotation tank. These skim just below the surface of the flotation tank removing the floated sludge containing contaminants into a separate trough for recovery.
The clarified water flows to the bottom of the flotation clarifying chamber and then to an effluent control weir for separation and collection
(D2) The sinking solids are collected in the hopper and these are then removed via a manual or automated valve
(E) The final treated and clarified effluent gets discharged into a sewage drain or for further treatment, as required

DAF is a preferred option as compared to sedimentation and other conventional settling techniques that use gravity for the removal of low-density particles that have a tendency to float, like oil and grease.
It offers several advantages like:
Other notable advantages of DAF include –
Low operation and maintenance
Modular system
Chemical
Robust Technology
DAF process is a physical process that is being used widely in wastewater treatment worldwide. It is used as a combination process usually along with coagulation.
The industries that use DAF for their wastewater treatment process are:
Dissolved air flotation is a popular and effective clarification process ideal for treating process and raw water with light particles, such as algae or colour-causing plants, oil and grease. It is also extremely useful when sedimentation does not work due to low temperatures.
DAF has been widely used for drinking water clarification in several European countries since decades.
The first DAF system for drinking water in the U.S. was installed in 1982 only. However, it wasn’t until the early 2000s that DAF became widely used in the United States.
DAF has become a mainstream clarifying process for drinking water treatment plants, especially where algae is prevalent.
It is also a popular pre-treatment process for seawater desalination systems to combat algal bloom occurrences globally.
DAF is a wastewater treatment of choice (especially in India) in several industrial processes where light-matter contaminants like oil. that don’t settle using sedimentation, need to be removed for getting CPCB compliant wastewater for discharge into the Municipal sewers.
Scott Ellyson, CEO of East West Manufacturing, brings decades of global manufacturing and supply chain leadership to the conversation. In this episode, he shares practical insights on scaling operations, navigating complexity, and building resilient manufacturing networks in an increasingly connected world.